4.9 KiB
DartMQ: A Message Queue System for Dart and Flutter
DartMQ is a Dart package that provides message queue functionality for sending messages between different components in your Dart and Flutter applications. It offers a simple and efficient way to implement message queues, making it easier to build robust and scalable applications.
Table of Contents
Introduction
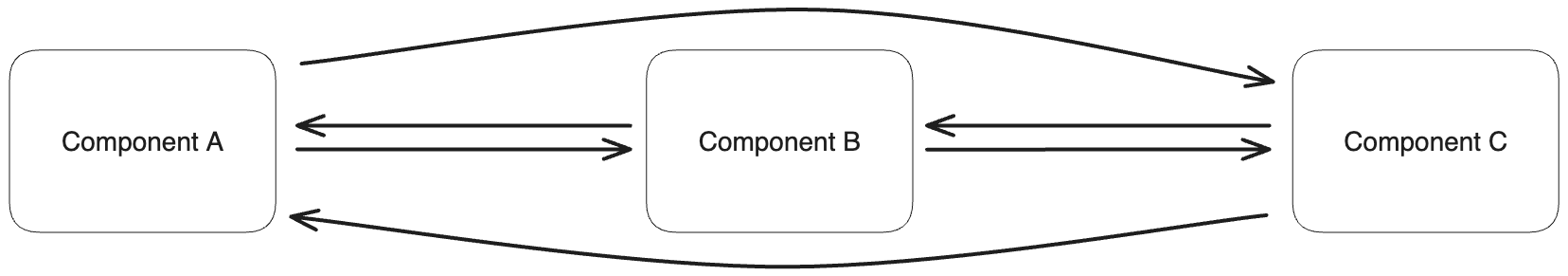
In the development of complex applications, dependencies among components are almost inevitable. Often, different components within your application need to communicate with each other, leading to tight coupling between these elements.
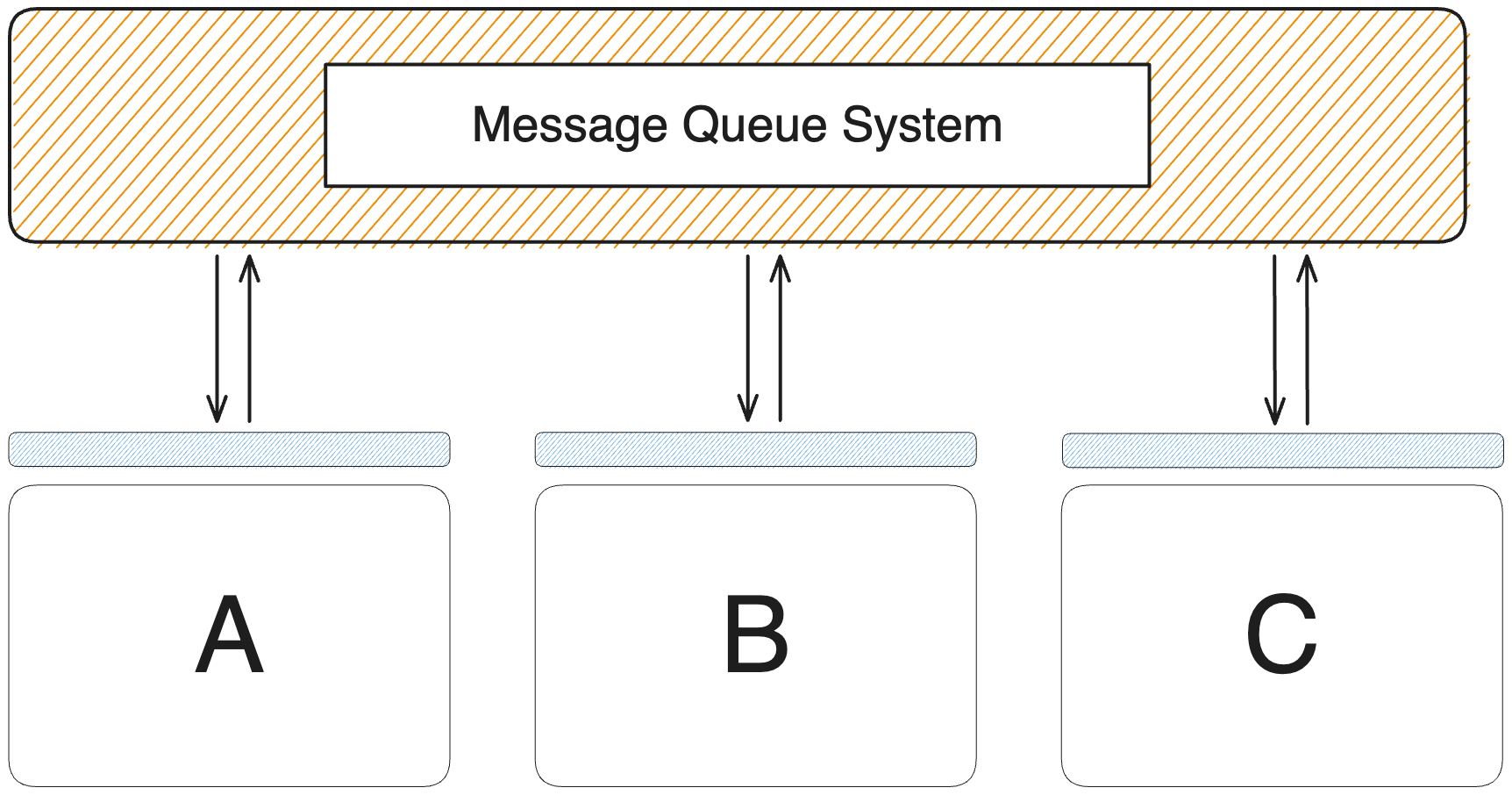
Message queues provide an effective means to decouple these components by enabling communication through messages. This decoupling strategy enhances the development of robust applications.
DartMQ employs the publish-subscribe pattern. Producers send messages, Consumers receive them, and Queues and Exchanges facilitate this communication.
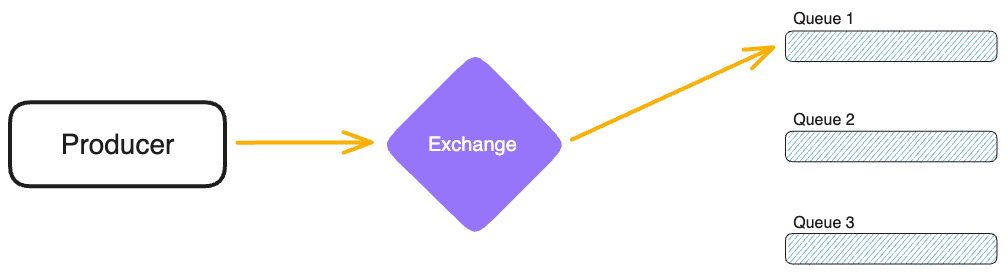
Communication channels are called Exchanges. Exchanges receive messages from Producers, efficiently routing them to Queues for Consumer consumption.
Exchanges
DartMQ provides different types of Exchanges for different use cases.
- Default Exchange: Routes messages based on Queue names.
- Fanout Exchange: Sends messages to all bound Queues.
- Direct Exchange: Routes messages to Queues based on routing keys.
Usage
Initialize an MQClient:
import 'package:dart_mq/dart_mq.dart';
void main() {
// Initialize DartMQ
MQClient.initialize();
// Your application code here
}
Declare a Queue:
MQClient.declareQueue('my_queue');
Note: Queues are idempotent, which means that if you declare a Queue multiple times, it will not create multiple Queues. Instead, it will return the existing Queue.
Create a Producer:
class MyProducer with ProducerMixin {
void greet(String message) {
// Send a message to the queue
sendMessage(
routingKey: 'my_queue',
payload: message,
);
}
}
Note:
exchangeNameis optional. If you don't specify an exchange name, the message is sent to the default exchange.
Create a Consumer:
class MyConsumer with ConsumerMixin {
void listenToQueue() {
// Subscribe to the queue and process incoming messages
subscribe(
queueId: 'my_queue',
callback: (message) {
// Handle incoming message
print('Received message: $message');
},
)
}
}
Putting it all together:
void main() {
// Initialize DartMQ
MQClient.initialize();
// Declare a Queue
MQClient.declareQueue('my_queue');
// Create a Producer
final producer = MyProducer();
// Create a Consumer
final consumer = MyConsumer();
// Start listening
consumer.listenToQueue();
// Send a message
producer.greet('Hello World!');
// Your application code here
...
}
Examples
-
Hello World: A simple example that demonstrates how to send and receive messages using DartMQ.
-
Message Filtering: An example that demonstrates how to multiple consumers can listen to the same queue and filter messages accordingly.
-
Routing: An example that demonstrates how to use Direct Exchanges to route messages to different queues based on the routing key.
-
RPC (Remote Procedure Call): An example that demonstrates how to send RPC requests and receive responses using DartMQ.
Acknowledgment
- RabbitMQ: This package is inspired by RabbitMQ, an open-source message-broker software that implements the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP).