165 lines
4.9 KiB
Markdown
165 lines
4.9 KiB
Markdown
# DartMQ: A Message Queue System for Dart and Flutter
|
|
|
|
<!-- TODO: fix pub version badge -->
|
|
|
|
[](https://pub.dev/packages/dart_mq)
|
|
[](https://app.codecov.io/gh/N-Razzouk/dart_mq)
|
|
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
|
|
|
|
DartMQ is a Dart package that provides message queue functionality for sending messages between different components in your Dart and Flutter applications. It offers a simple and efficient way to implement message queues, making it easier to build robust and scalable applications.
|
|
|
|
## Table of Contents
|
|
|
|
1. [Introduction](#introduction)
|
|
2. [Exchanges](#exchanges)
|
|
3. [Usage](#usage)
|
|
4. [Examples](#examples)
|
|
5. [Acknowledgment](#acknowledgment)
|
|
|
|
###
|
|
|
|
## Introduction
|
|
|
|
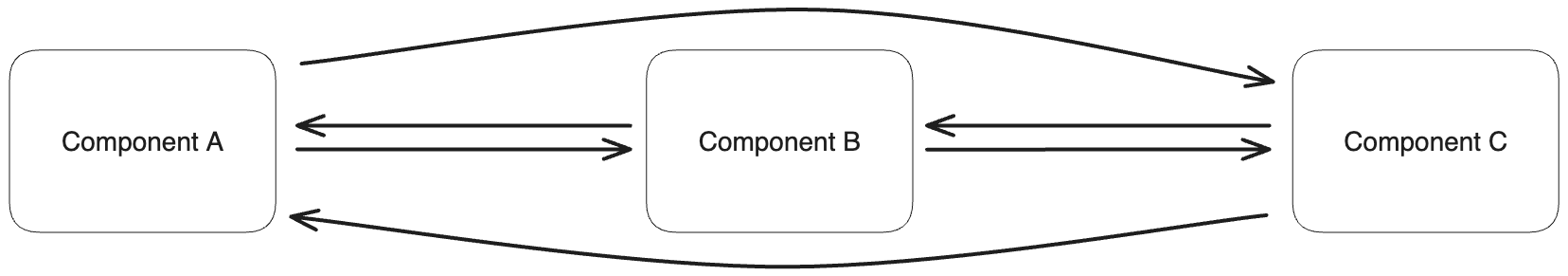
In the development of complex applications, dependencies among components are almost inevitable. Often, different components within your application need to communicate with each other, leading to tight coupling between these elements.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
###
|
|
|
|
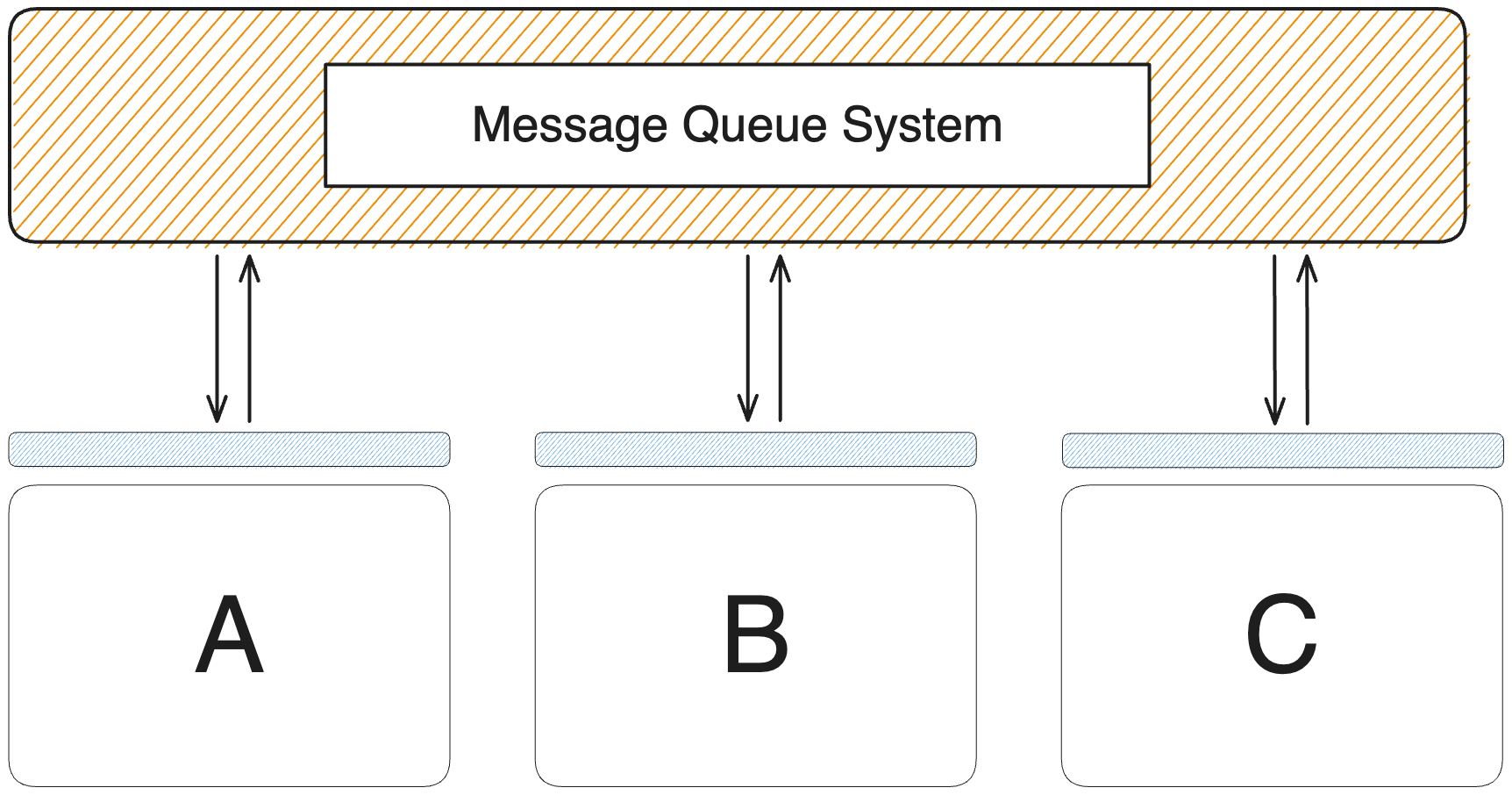
Message queues provide an effective means to decouple these components by enabling communication through messages. This decoupling strategy enhances the development of robust applications.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
###
|
|
|
|
DartMQ employs the publish-subscribe pattern. **Producers** send messages, **Consumers** receive them, and **Queues** and **Exchanges** facilitate this communication.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
###
|
|
|
|
Communication channels are called Exchanges. Exchanges receive messages from Producers, efficiently routing them to Queues for Consumer consumption.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
## Exchanges
|
|
|
|
### DartMQ provides different types of Exchanges for different use cases.
|
|
|
|
###
|
|
|
|
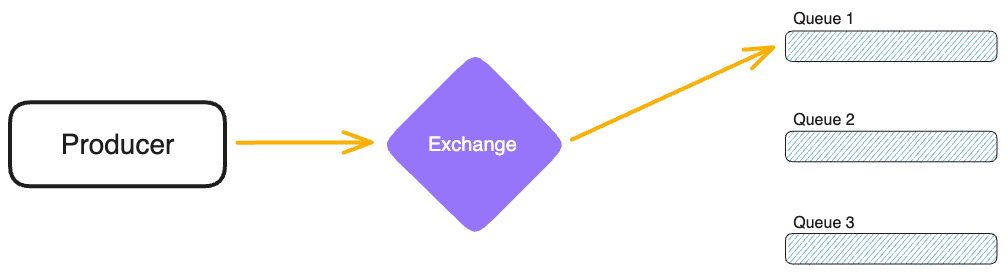
- **Default Exchange**: Routes messages based on Queue names.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
###
|
|
|
|
- **Fanout Exchange**: Sends messages to all bound Queues.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
###
|
|
|
|
- **Direct Exchange**: Routes messages to Queues based on routing keys.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
## Usage
|
|
|
|
### Initialize an MQClient:
|
|
|
|
<!-- TODO: change import in code snippet. -->
|
|
|
|
```dart
|
|
import 'package:dart_mq/dart_mq.dart';
|
|
|
|
void main() {
|
|
// Initialize DartMQ
|
|
MQClient.initialize();
|
|
|
|
// Your application code here
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Declare a Queue:
|
|
|
|
```dart
|
|
MQClient.declareQueue('my_queue');
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
> Note: Queues are idempotent, which means that if you declare a Queue multiple times, it will not create multiple Queues. Instead, it will return the existing Queue.
|
|
|
|
### Create a Producer:
|
|
|
|
```dart
|
|
class MyProducer with ProducerMixin {
|
|
void greet(String message) {
|
|
// Send a message to the queue
|
|
sendMessage(
|
|
routingKey: 'my_queue',
|
|
payload: message,
|
|
);
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
> Note: `exchangeName` is optional. If you don't specify an exchange name, the message is sent to the default exchange.
|
|
|
|
### Create a Consumer:
|
|
|
|
```dart
|
|
class MyConsumer with ConsumerMixin {
|
|
void listenToQueue() {
|
|
// Subscribe to the queue and process incoming messages
|
|
subscribe(
|
|
queueId: 'my_queue',
|
|
callback: (message) {
|
|
// Handle incoming message
|
|
print('Received message: $message');
|
|
},
|
|
)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Putting it all together:
|
|
|
|
```dart
|
|
void main() {
|
|
// Initialize DartMQ
|
|
MQClient.initialize();
|
|
|
|
// Declare a Queue
|
|
MQClient.declareQueue('my_queue');
|
|
|
|
// Create a Producer
|
|
final producer = MyProducer();
|
|
|
|
// Create a Consumer
|
|
final consumer = MyConsumer();
|
|
|
|
// Start listening
|
|
consumer.listenToQueue();
|
|
|
|
// Send a message
|
|
producer.greet('Hello World!');
|
|
|
|
// Your application code here
|
|
...
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Examples
|
|
|
|
- [Hello World](example/hello_world): A simple example that demonstrates how to send and receive messages using DartMQ.
|
|
|
|
- [Message Filtering](example/message_filtering): An example that demonstrates how to multiple consumers can listen to the same queue and filter messages accordingly.
|
|
|
|
- [Routing](example/routing): An example that demonstrates how to use Direct Exchanges to route messages to different queues based on the routing key.
|
|
|
|
- [RPC (Remote Procedure Call)](example/rpc): An example that demonstrates how to send RPC requests and receive responses using DartMQ.
|
|
|
|
## Acknowledgment
|
|
|
|
- [RabbitMQ](https://www.rabbitmq.com/): This package is inspired by RabbitMQ, an open-source message-broker software that implements the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP).
|